When I first saw the message Pre-Memory CPU Initialization is started, I was confused. But I learned it’s just the computer’s way of checking that everything, especially the memory, is ready before fully starting up.
Pre-Memory CPU Initialization Is Started (short answer)
Yes, pre-memory CPU Initialization refers to the computer’s checking and preparing memory before the full startup. This step ensures that essential hardware components function correctly, allowing the system to boot smoothly.
In this article, we will explore the process of Pre-Memory CPU Initialization.
What Is CPU Initialization?
CPU initialization is the process when the computer is turned on. The CPU checks all the parts of the computer, like memory and storage, to make sure they work. Then, it starts the system software so the computer can run and be ready for use.
What Is Pre-Memory?
Pre-memory is the early stage in a computer’s startup when the CPU checks and prepares the basic hardware, like the memory (RAM) before the main system starts. It ensures everything is ready so the computer can load the operating system and start working properly.
Why Pre-Memory CPU Initialization Error Occurs?
A pre-memory CPU initialization error happens when the CPU can’t properly check or prepare the computer’s memory (RAM) during startup. This could be due to faulty RAM, incorrect settings, or problems with the motherboard, causing the computer to stop working before loading the system.
Pre-Memory CPU Initialization Is Started:
Pre-memory CPU initialization is started” means the CPU has begun its early checks and setup process, focussing on preparing the memory (RAM) before the main system starts running. This step ensures that everything is ready for the computer to continue booting up properly.
Read Also: CPU How Hot Is Too Hot – A Detailed Overview!
Fix #01 To Resolve Pre Memory Cpu Initialization?
We will discuss Resolve Pre-Memory CPU Initialization.
Step 1: Disable Overclocking:
Disabling overclocking means turning off any settings that make your computer’s processor or memory run faster than usual. This can help fix issues if the computer is having problems because the components are pushed too hard. It ensures everything runs at safe, normal speeds.
Step 2: Reset the BIOS (CMOS Clear):
Resetting the BIOS (CMOS clear) means returning the computer’s settings to their original state. This is done by removing the battery from the motherboard or using a jumper on it. It helps fix problems caused by incorrect settings, making the computer start fresh.
Step 3: Minimal Configuration:

Minimal configuration means starting the computer with just the essential parts, like the CPU, one RAM stick, and storage. This helps to see if adding extra parts is causing problems by using only the basic components needed to start the system.
Step 4: Boot the PC:
Booting the PC means turning on the computer and starting its operating system. This process loads the software and gets everything ready so you can use the computer for tasks like browsing the internet or running programs.
Step 5: Gradual Component Testing:
Gradual component testing means checking each part of the computer one by one. You start with the basic setup, then add one component at a time to see if it causes any problems. This helps identify which part might be faulty.
Step 6: Full System Assembly:
Full system assembly means putting together all the parts of a computer, including the CPU, RAM, storage, motherboard, and other components, into a complete, working system. It’s the final step in building or repairing a computer to ensure everything is connected and functions properly.
Fix #02: To Resolve Pre-Memory CPU Initialization?
We will discuss Fix #02 to Resolve Pre-Memory CPU Initialization.
Step 1: Probe Removal:
Probe removal means taking out or disconnecting any diagnostic tools or test devices that were used to check the computer’s components. This step is done after testing is complete to ensure the computer is ready for normal use.
Step 2: Check the CPU socket:
Checking the CPU socket means inspecting the place on the motherboard where the CPU is installed. You look for any bent pins, dirt, or other issues that might cause a bad connection. This ensures the CPU is properly seated and can work correctly.
Step 3: Memory Seating:
Memory seating means ensuring that the RAM modules are properly inserted into their slots on the motherboard. If the memory isn’t seated correctly, the computer may not recognize it, leading to startup problems or performance issues.
Step 4: CPU Cooler Inspection
CPU cooler inspection involves checking the cooling system attached to the CPU to ensure it is properly mounted, free of dust, and functioning correctly. This helps prevent overheating, which can cause the computer to slow down or shut off unexpectedly.
Step 5: Power Supply Connections:
Power supply connections refer to making sure all the cables from the power supply are securely connected to the motherboard and other components like the CPU, GPU, and storage devices. Proper connections are essential for the computer to receive power and function correctly.
Step 6: Simplified Setup
A simplified setup means arranging or configuring a computer with only the basic parts needed to start it. This helps make sure everything works properly before adding extra components.
Step 7: BIOS Reset:
BIOS reset means returning the computer’s BIOS settings to their original defaults. This can help fix issues caused by incorrect settings and ensure the computer starts up correctly.
Step 8: GPU Check:
A GPU check involves inspecting the graphics card to ensure it is properly installed and functioning. This includes looking for loose connections, checking for any visible damage, and making sure it’s working correctly to handle graphics and display tasks.
Step 9: Monitor Input:
Monitor input refers to checking and selecting the correct source or connection on your monitor. It ensures that the monitor is receiving the signal from the right device, like a computer or a gaming console, so you can see the display properly.
Read Also: Is It Normal For CPU Clock Speed To Fluctuate? Detailed Guide!
Fix #03: To Resolve Pre-Memory CPU Initialization?
We will discuss Fix #03 to Resolve Pre-Memory CPU Initialisation.
Step 1: Reseat the RAM:
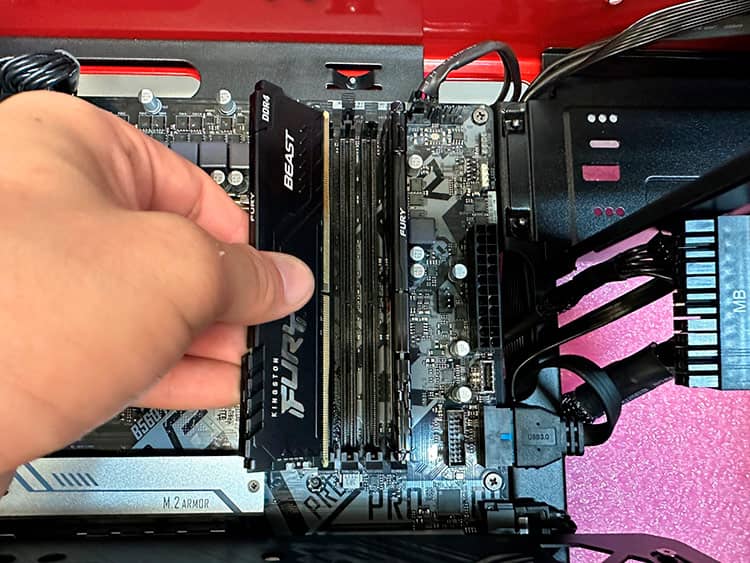

Reseat the RAM means removing the memory sticks from their slots on the motherboard and then reinserting them securely. This can solve issues if the computer isn’t detecting the RAM correctly or has trouble starting up.
Step 2: Try a Single RAM Stick:
Try a single RAM stick means using just one memory stick in the computer instead of multiple. This helps identify if a faulty RAM stick is causing issues, allowing you to test each one individually for problems.
Step 3: Check for Loose Connections:
Checking for loose connections means inspecting all the cables and components inside your computer to make sure everything is securely plugged in. Loose connections can cause problems with power, data, or performance, so tightening them can help fix issues.
Step 4: Inspect for Bent CPU Pins:
Inspecting bent CPU pins means carefully looking at the small pins on the bottom of the CPU to see if any are bent or damaged. Bent pins can prevent the CPU from connecting properly to the motherboard, causing the computer not to work correctly.
Step 5: Test With Minimal Hardware:
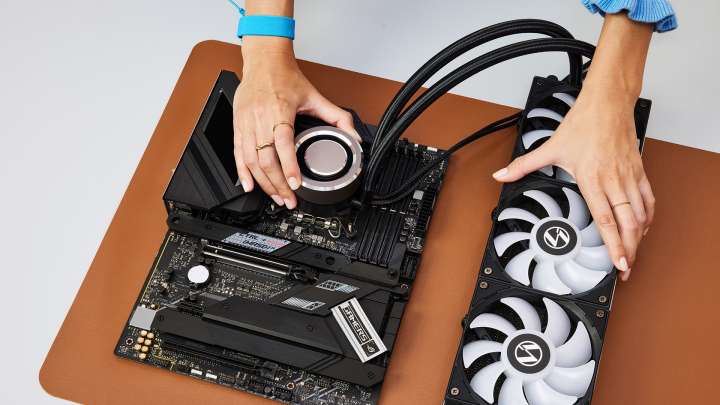

Testing with minimal hardware means starting the computer with only the essential parts, like the CPU, one RAM stick, and basic storage. This helps identify if any extra components are causing issues by simplifying the system to its basic needs.
Step 6: Try a Different GPU Slot:
Try a different GPU slot means removing your graphics card (GPU) from its current slot on the motherboard and inserting it into another available slot. This helps determine if the original slot is faulty or causing display issues.
Step 7: Monitor Your PSU:
Monitoring your PSU means keeping an eye on your power supply unit (PSU) to ensure it’s delivering the right amount of power to your computer. A failing PSU can cause random shutdowns, performance issues, or prevent the computer from starting.
Step 8: Inspect for Physical Damage:
Inspecting for physical damage means carefully checking your computer’s components, like the motherboard, CPU, and cables, for any visible signs of wear, cracks, or damage. Identifying physical damage early can help prevent bigger issues and keep your computer running smoothly.
Step 9: Check for BIOS Updates:
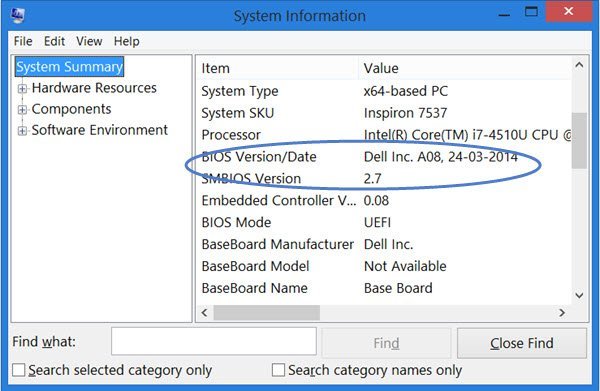
Check for BIOS updates means looking for newer versions of the BIOS software provided by your motherboard’s manufacturer. Updating the BIOS can fix bugs, improve system stability, and support new hardware, ensuring your computer runs more efficiently.
Step 10: Contact Manufacturer Support:
Contacting manufacturer support means reaching out to the company that made your computer or its parts for help. They can provide expert advice, troubleshooting steps, or repairs if you’re experiencing issues that you can’t resolve on your own.
Read Also: Are Odd Cores On My CPU My Non-Hyperthreaded Cores? The Guide of 2024
What Is The Benefit Of Pre-Memory CPU Initialization Being Started?
The benefit of pre-memory CPU Initialization being started is that it ensures the computer’s memory and essential hardware are properly checked and prepared before the system fully starts, leading to a more stable and reliable boot process.
The Significance Of Pre-Memory CPU Initialization
The importance of pre-memory CPU Initialization lies in its role of checking and preparing the computer’s memory before starting up. This ensures that all hardware components are working properly, allowing the system to boot smoothly without issues.
Error Code 15 Pre Memory System Agent Initialization Is Started?
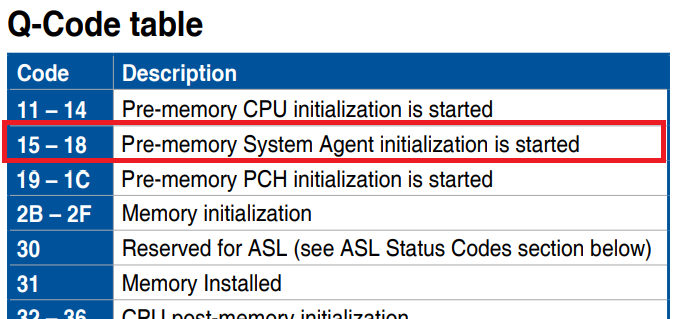
Error Code 15, “Pre-Memory System Agent Initialization is started,” indicates that the computer is checking the system agent, which manages communication between the CPU and memory, before fully starting up. If there’s an issue, it might mean a problem with the memory or CPU connection.
Expo Delays Boot Up By 1min With “Pre-Memory System Agent Initialization Is Started” But Works Fine After Boot
If enabling EXPO slows your boot by 1 minute with the message “Pre-Memory System Agent Initialization is started,” it’s likely the system adjusting memory settings for overclocking. This delay is normal to ensure stability before starting up fully.
Unable to Initialize Memory With Z690 Motherboards Unable To Boot To Bios, Stuck At Q-Code 11
If your Z690 motherboard is stuck at Q-Code 11 due to memory issues, try reseating the RAM, testing different slots, using one RAM stick, clearing CMOS, checking compatibility, updating the BIOS, or testing with different RAM to fix the problem.
Msi Debug Code 19, Early South Bridge Initialization
MSI Debug Code 19, “Early South Bridge Initialization,” indicates a problem during the early setup of the South Bridge on the motherboard. This part manages connections between the CPU, memory, and other components, and issues here can prevent the computer from starting properly.
Pre Memory CPU initialization is started in Windows 11
“Pre-Memory CPU Initialization is Started” in Windows 11 refers to the initial phase of the computer’s startup process where the CPU checks and prepares the memory before the operating system fully loads. This step ensures that all essential hardware components are ready for Windows 11 to boot smoothly.
Motherboard Error Code List
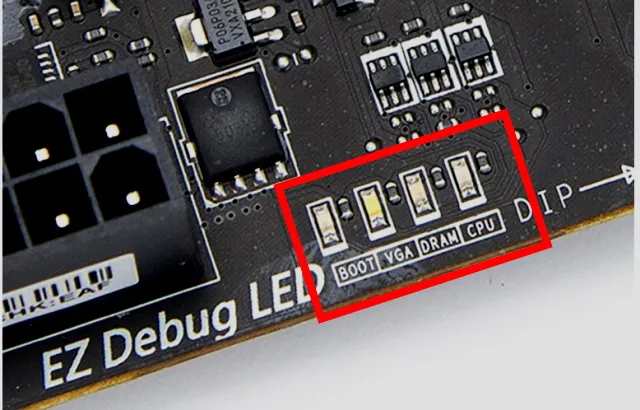
Motherboard error codes help find hardware issues. Common codes: “00” means CPU problem, “55” signals RAM issue, and “A2” shows storage device trouble. Beep sounds also indicate problems, like one beep is good, while many suggest errors.
Pch Initialization After Microcode Loading
“PCH Initialization After Microcode Loading” means the motherboard is setting up the Platform Controller Hub (PCH) after loading the CPU’s instructions. This helps the CPU connect with storage, USB ports, and other parts before the system starts fully.
CPU Post-Memory Initialization
CPU Post-Memory Initialization” means the CPU is set up after the memory check is done. It ensures everything with the memory is ready before moving on to the next steps of starting the computer.
How Do I Fix CPU Post Memory Initialization?
To fix CPU post-memory initialization issues, follow these steps:
- Check RAM seating: Ensure the memory sticks are properly seated.
- Test RAM modules: Try using one RAM stick at a time.
- Clear CMOS: Reset the BIOS.
- Update BIOS: Install the latest version.
What Is Code 14 On Asus X670e Hero?
Code 14 on the ASUS X670E Hero motherboard typically means the system is in the “Pre-memory CPU initialization” phase. This is part of the boot process where the CPU is being checked before the memory setup starts. If the system hangs on this code, it may suggest issues with the CPU, power delivery, or BIOS configuration.
To troubleshoot:
- Check CPU seating and connections.
- Reset BIOS by clearing CMOS.
- Update BIOS to the latest version.
- Check the power supply and cables for proper connection.
FAQ,s
1. Why is pre-memory CPU initialization important?
Pre-memory CPU initialization is important because it checks the CPU before the memory starts working. This helps ensure the CPU is ready, preventing problems during the system’s boot process.
2. What is pre-memory CPU initialization?
Pre-memory CPU initialization is the process where the computer checks if the CPU is working correctly before setting up the memory (RAM). It happens early in the boot process to ensure the system runs smoothly.
3. How long does pre-memory CPU initialization take?
Pre-memory CPU initialization usually takes a few seconds. If it takes too long or seems stuck, it might indicate a problem with the CPU, RAM, or other hardware.
4. What happens during pre-memory CPU initialization?
During pre-memory CPU initialization, the system performs several checks:
- CPU Check: Verifies if the CPU is properly installed and functional.
- Basic Setup: Initializes essential CPU functions needed for the next steps.
- Hardware Detection: Confirms that the CPU can communicate with other components.
- Preparation: Prepares the system to start setting up memory and other hardware.
This step ensures the CPU is ready before the system moves on to load and check memory.
5. What causes CPU error?
CPU errors can be caused by:
- Overheating: High temperatures can damage or disrupt CPU function.
- Improper Installation: A loose or incorrectly installed CPU can lead to errors.
- Power Issues: Insufficient or unstable power supply can affect CPU performance.
- Faulty Hardware: Defective CPU or related components like motherboard or RAM.
- BIOS Problems: Outdated or corrupt BIOS settings may cause CPU errors.
- Overclocking: Excessive overclocking can push the CPU beyond its limits.
6. What is CPU post-memory initialization error 32?
CPU post-memory initialization error 32 means there’s a problem with the memory setup after the CPU check. It could be caused by faulty RAM, incorrect seating, or BIOS settings needing adjustment.
7. How do I fix my CPU memory?
To fix CPU memory issues, try these steps:
- Check RAM seating: Ensure memory sticks are properly inserted.
- Test RAM sticks: Use one at a time to find faulty modules.
- Clear CMOS: Reset BIOS settings.
- Update BIOS: Install the latest version.
- Replace RAM: If faulty, consider new memory.
8. Can pre-memory CPU initialization be skipped?
Pre-memory CPU initialization cannot be skipped because it’s a necessary step. It checks if the CPU works properly before setting up memory, helping ensure the system runs without problems.
9. How Do I Reset My CPU RAM?
To reset your CPU RAM, turn off your computer, remove the RAM sticks, and then reinstall them securely. You can also reset the BIOS by clearing the CMOS to refresh all memory settings.
10. What Does Reset CMOS Do?
Resetting CMOS clears the BIOS settings and returns them to default. This helps fix problems like boot errors or incorrect hardware configurations, allowing the system to start fresh with factory settings.
11. Misteria of the Old Computer Or Constantly Looping On Pre-memory north-bridge initialization is started
The mystery of an old computer looping on “Pre-memory North-Bridge initialization is started” means it’s stuck trying to connect the CPU and memory. Causes include faulty hardware, wrong BIOS settings, overclocking issues, or a weak power supply.
12. Maximus Gene VII Q Code 15 (Pre-memory System Agent initialization is started)
Maximus Gene VII Q Code 15 means the system is stuck at “Pre-memory System Agent initialization is started.” This checks the memory controller before the system starts. Fix it by checking RAM seating, testing modules, clearing CMOS, or updating BIOS.
Conclusion
Pre-memory CPU initialization is a critical but often overlooked part of your computer’s startup process. By ensuring that your CPU is properly initialized, you can prevent hardware issues, improve performance, and enjoy a smoother, more reliable computing experience. Keeping your BIOS updated and understanding the basics of this process can help you get the most out of your system. and ready for the system to boot up properly.
Also Read
- CPU How Hot Is Too Hot – A Detailed Overview!
- Is It Normal For CPU Clock Speed To Fluctuate? Detailed Guide!
- Are Odd Cores On My CPU My Non-Hyperthreaded Cores? The Guide of 2024