The first time I noticed corrosion on a CPU, I was surprised! I always thought computer parts were solid. But seeing small, rusty spots made me realize how delicate they are. Now I take extra care to protect them from humidity and dust.
Corrosion on CPU (Short answer)
Corrosion occurs when moisture or dust affects a CPU’s metal parts, causing rust and weakening connections. This can lower performance and even damage the CPU. Proper care and maintenance help prevent corrosion issues.
In this article, we will discuss corrosion on the CPU.
What Is Corrosion On A CPU?
Corrosion is a natural process in which metals deteriorate due to chemical reactions with the environment, especially when exposed to moisture and oxygen. If not addressed early, corrosion can lead to weakened connections, reduced performance, or even total hardware failure for CPUs.
Causes of Corrosion on CPUs
Corrosion on CPUs can happen due to several factors:
- Humidity and moisture exposure: High humidity levels can lead to condensation on sensitive electronic components.
- Electrochemical Reactions: When metals on the CPU come into contact with certain substances, they can trigger a reaction that degrades the metal.
- Improper Maintenance and Handling: Touching the CPU with bare hands, using low-quality cleaning agents, or applying excessive force can lead to exposure and corrosion over time.
Types of Corrosion on CPUs
Different types of corrosion can affect a CPU, each with unique characteristics and levels of damage:
- Surface corrosion: visible to the naked eye, this is often found on CPU pins or exposed metal parts.
- Internal Corrosion: Occurs within the CPU’s structure and is harder to detect but can lead to serious damage.
- Galvanic Corrosion: This happens when two metals with different electric potentials come into contact, causing one to corrode faster than the other.
How To Detect Corrosion On A CPU?
Detecting corrosion early can save your CPU from extensive damage. Here are some methods:
- Visual Inspection: Look for signs of discoloration or residue on the CPU’s metal parts.
- Diagnostic Tools: Some software tools can analyze CPU performance and flag unusual behavior that may indicate corrosion.
How To Clean Cpu Pin Corrosion?
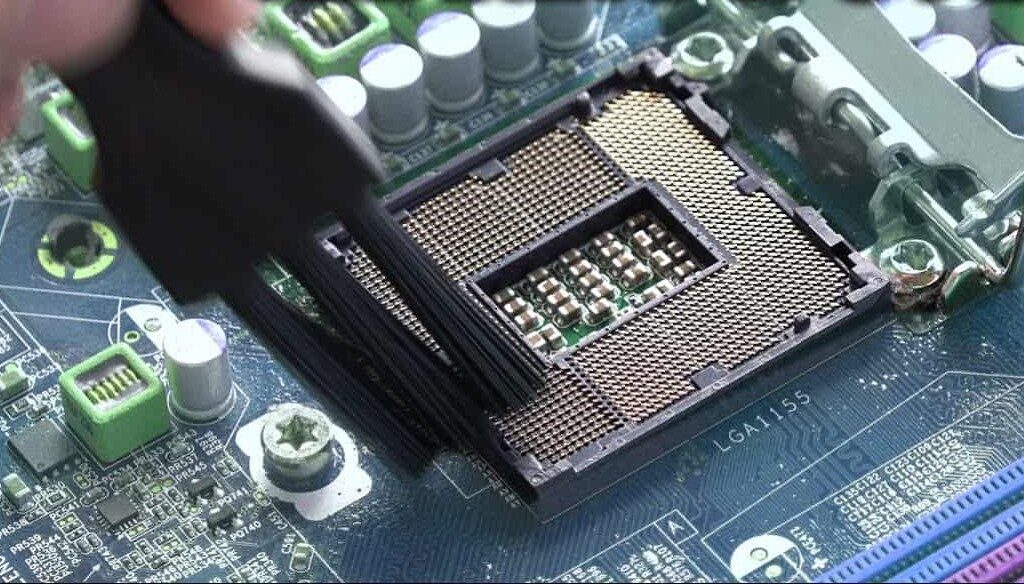
To clean CPU pin corrosion, follow these steps:
- Gather Supplies: You’ll need isopropyl alcohol (90% or higher), a soft toothbrush or cotton swabs, and a lint-free cloth.
- Power Off and Disconnect: Turn off your computer and disconnect all power sources before handling the CPU.
- Apply Isopropyl Alcohol: Dampen the toothbrush or a cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol.
- Gently Clean: Carefully brush the corroded pins with the alcohol-soaked tool, using light pressure to avoid bending or damaging the pins.
- Wipe Away Residue: Use a lint-free cloth to remove any remaining corrosion or alcohol residue.
- Let It Dry: Allow the CPU to dry completely before reinstalling it into the motherboard.
- Check for Damage: Inspect the pins for any signs of damage. Consider consulting a professional or replacing the CPU if the corrosion is severe or the pins are bent.
Following these steps can help restore your CPU’s performance and prevent further issues.
Impact of Corrosion on CPU Performance
Corrosion can reduce CPU efficiency, causing slower processing speeds and increasing the likelihood of crashes or unexpected shutdowns. If left untreated, corrosion could lead to complete CPU failure, requiring expensive replacements.
Corrosion in CPU Pins vs. Other Components
CPU pins are particularly vulnerable to corrosion because of their small size and close arrangement. Pins connect the CPU to the motherboard, so corrosion here can disrupt connections and interfere with performance. Other components like the motherboard or GPU may also suffer from corrosion but are typically less vulnerable than CPU pins.
Choosing the Right Thermal Paste
Thermal paste quality plays a big role in keeping corrosion away from CPUs. High-quality thermal paste helps in maintaining efficient heat dissipation and protecting against moisture. Types of thermal pastes that are less likely to contribute to corrosion include silicone-based or carbon-based pastes.
Protective Coatings and Materials for CPUs
Several anti-corrosion coatings are available for CPUs. These coatings add a layer of protection to metal surfaces, slowing down the corrosion process. Materials that are naturally resistant to corrosion, like stainless steel or gold-plated components, are also excellent options for sensitive parts.
Repairing a Corroded CPU

Repairing a corroded CPU can be tricky, but minor corrosion can sometimes be managed at home. Clean the affected area with isopropyl alcohol and a soft brush, taking care not to apply too much pressure. If corrosion is extensive, consider consulting a professional technician.
Common Myths About CPU Corrosion
There are several myths surrounding CPU corrosion:
- Myth: Corrosion only happens in old CPUs.
- Fact: Corrosion can occur in both old and new CPUs if environmental conditions are unfavorable.
- Myth: You can prevent all corrosion with frequent cleaning.
- Fact: While cleaning helps, controlling humidity and using quality thermal paste is also essential.
How To Store Your CPU Safely?
Proper storage conditions help reduce the risk of corrosion. CPUs should be stored in cool, dry places, away from direct sunlight. Keeping the CPU in a climate-controlled environment is ideal for long-term storage.
Using anti-static bags and other storage tips
Anti-static bags help protect CPUs from both static electricity and environmental factors that can cause corrosion. These bags are easy to find and provide an inexpensive way to safeguard your CPU when it’s not in use.
[Solved] Rust/Corrosion in CPU Pins. How To Handle It?
If you spot rust or corrosion on CPU pins, clean them gently with isopropyl alcohol and a soft brush. Ensure that the CPU is thoroughly dried before putting it back in place.If corrosion is severe, consider professional repair or replacement.
Preventing Electronics Corrosion on Computers, Integrated Circuits, and Microchips?
To prevent corrosion on computers, integrated circuits, and microchips, follow these tips:
- Control Humidity: Keep your workspace dry and use dehumidifiers if necessary to reduce moisture in the air.
- Temperature Management: Avoid extreme temperature fluctuations, as heat can attract moisture.
- Proper Storage: Store electronics in anti-static bags and in a cool, dry environment when not in use.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean components regularly with a soft brush or cloth to remove dust and debris that can hold moisture.
- Use Quality Thermal Paste: Apply good-quality thermal paste to help manage heat and prevent moisture buildup.
- Protective Coatings: Consider using conformal coatings on sensitive components to add a layer of protection against moisture and corrosion.
By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of corrosion and extend the life of your electronics.
How Do Vci Capsules Prevent Electronics Corrosion?
VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) capsules prevent electronic corrosion by releasing protective vapors that inhibit rust and corrosion on metal surfaces. When placed in storage or shipping environments, these capsules create a protective atmosphere that coats the surfaces of electronic components, blocking moisture and corrosive elements.
This helps extend the lifespan of electronics by keeping them safe from environmental factors that can cause damage.
I Need Advice On Corrosion Removal And Prevention On Old CPU Legs + Top
Here’s some advice on removing and preventing corrosion on old CPU legs and the top:
Corrosion Removal
- Gather Materials: You will need isopropyl alcohol (90% or higher), a soft toothbrush or cotton swabs, and a lint-free cloth.
- Power Off and Disconnect: Ensure the computer is turned off and unplugged before handling the CPU.
- Clean the Pins:
- Dampen the toothbrush or cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol.
- Gently scrub the corroded areas on the CPU legs, applying light pressure to avoid bending the pins.
- Clean the Top:
- Use the same alcohol-dampened brush or cloth to wipe the top surface of the CPU.
- Be careful around any sensitive components.
- Dry Completely: Allow the CPU to air dry completely before reinstalling it.
- Inspect for Damage: After cleaning, check for any bent or damaged pins. If there’s significant damage, consider consulting a professional or replacing the CPU.
Corrosion Prevention
- Control Environment: Store your CPU in a cool, dry place to minimize humidity exposure.
- Use Anti-Static Bags: When not in use, keep the CPU in an anti-static bag to protect it from moisture and dust.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically check and clean your CPU and other components to prevent dust and moisture buildup.
- Apply protective coatings: Consider using conformal coatings on exposed metal areas for added protection against moisture.
- Avoid Handling: Minimize touching the CPU directly, especially if your hands are moist or dirty.
By following these steps, you can effectively clean and help prevent corrosion on your old CPU legs and the top, extending its lifespan and performance.
What Type of Corrosion Happens in a Computer? How Does It Affect How The Computer Works?
In computers, several types of corrosion can occur, mainly involving the metal parts:
- Rust (oxidation): This is the most common type, especially on iron and steel components. It occurs when these metals react with moisture and oxygen, forming rust.
- Electrolytic Corrosion: This happens when different metals are in contact with the presence of an electrolyte (like moisture). It can cause one metal to corrode faster than the other.
- Tarnishing: This typically affects copper and silver components. It creates a layer of corrosion that can impede conductivity.
Effects on Computer Performance
- Electrical Connections: Corrosion can lead to poor electrical connections, which may cause intermittent failures, reduced performance, or complete failure of components.
- Heat Dissipation: Corroded surfaces may affect heat transfer, leading to overheating, which can reduce the lifespan of components and cause thermal throttling.
- Signal Interference: Corrosion can alter the electrical pathways in circuits, leading to signal degradation and erratic behavior in devices.
- Complete Failure: In severe cases, corrosion can render a component completely inoperable, necessitating repairs or replacements.
Overall, corrosion can significantly impact the reliability and performance of a computer, highlighting the importance of proper maintenance and environmental control.
FAQ,s
1. How Do I Know If My CPU Is Corroding?
Look for discoloration or residue on metal parts, especially around the pins. Diagnostic tools can also help detect performance issues due to corrosion.
2. Can I fix CPU corrosion myself?
Minor corrosion can sometimes be cleaned at home with isopropyl alcohol, but serious corrosion should be handled by professionals.
3. Does corrosion affect other computer components?
Yes, corrosion can also impact components like the motherboard and GPU, but CPU pins are particularly vulnerable.
4. What Type Of Thermal Paste Is Best For Preventing Corrosion?
Silicone-based or carbon-based thermal pastes are generally better at reducing corrosion risk.
5. Are There Coatings To Protect Cpus From Corrosion?
Yes, anti-corrosion coatings are available and can be applied to metal surfaces to slow down corrosion.
6. How To Remove Corrosion From A CPU?
To remove corrosion from a CPU, gently clean the affected areas with a cotton swab dipped in 90%+ isopropyl alcohol. Use a soft brush for stubborn spots, and let it dry fully before reinstalling. For heavy corrosion, consult a professional.
7. Can A CPU Corrode?
Yes, a CPU can corrode. Exposure to moisture, humidity, and dust can cause its metal parts, especially the pins, to corrode over time, leading to weaker connections and potential performance issues.
8. Does corrosion ruin electronics?
Yes, corrosion can ruin electronics by damaging metal parts, weakening connections, and causing short circuits. Over time, this can lead to poor performance, malfunctions, or even complete failure of the device.
9. What Is The Grey Stuff On My Cpu?
The gray stuff on your CPU is likely thermal paste or thermal compound, used to improve heat transfer between the CPU and its cooler. If it looks dried out or discolored, it might be time to clean it off and apply a fresh layer.
10. Could This Be Corrosion/Rust On My CPU Block?
Yes, the gray or discolored spots on your CPU block could be corrosion or rust, especially if it’s metal. This can happen due to moisture exposure. It’s important to clean it carefully and check for any potential damage to ensure proper cooling and performance.
11. My CPU Is Corrosion, Any Way To Save It?
If your CPU has corrosion, you can try to save it by gently cleaning the affected areas with isopropyl alcohol and a soft brush. Make sure it dries completely before using it again. However, if the corrosion is severe or if you’re unsure, it’s best to consult a professional or consider replacing the CPU.
Conclusion
Corrosion on a CPU can have a significant impact on performance and longevity. By understanding the causes and prevention strategies, you can protect your CPU and keep it running smoothly for longer. Regular cleaning, choosing the right thermal paste, and controlling the environment are all effective ways to prevent corrosion.



